Voluntary Carbon Certificates
SCHOLAS MACOMA
SCHOLAS MACOMA – Communis Domus program on Voluntary Carbon Certificates
- Voluntary Carbon Certificates (VCC) allow for the trading of credits without government regulations. This means that individuals, businesses, and non-profits looking to reduce or eliminate their greenhouse gas emissions can take part.
- Participants can buy VCC’s to compensate for their carbon footprint, whether driven by a desire to support environmental initiatives or to meet corporate sustainability goals.
- The VCC mobilizes private capital, directs investment toward climate mitigation activities, and offers funding for crucial climate mitigation endeavors.
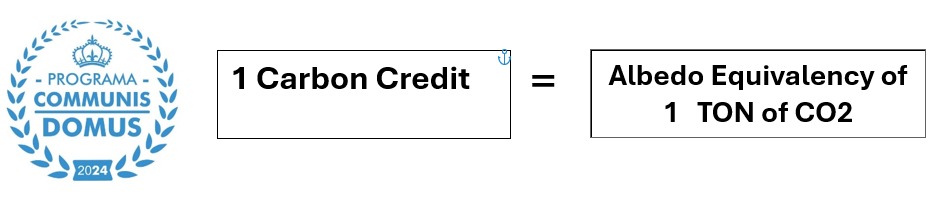
To put this into a simple perspective we need an average of 30 trees to offset 1 ton of CO2
According to scientific studies, it can take between 31vto 46 trees to offset 1 ton of carbon dioxide (CO2) per year., depending on the tree type, season, and location. For example, a hardwood tree can absorb up to 48 pounds of CO2 per year, and by the time it’s 40 years old, it can sequester about 1 ton of CO2.
Cool Roof benefits:
100 m2 (1,000 sq. ft.) of Cool Roof offsets an equivalent of an average of 28 ton of CO2
Which equals to 840 trees, and this is an equivalent of 1 hectare (2.5 acres of forest)
The Itaembe Guazu Cool Roof Project will offset an equivalent of 252,000 MT of CO2. In addition, the highly reflective cool roof coating will benefit 12,000 low-income homes by reducing interior temperatures, roof temperature, and urban heat island effect.
VCC benefit
Investing in Voluntary Carbon Certificates (VCC) offers numerous benefits. It incentivizes businesses to immediately and in the long term lower their emissions, thus promoting global sustainability by encouraging investment in research and development for innovative emission reduction or equivalency strategies.
Funding Climate Solutions:
Voluntary Carbon Credits (VCCs) can help fund environmental initiatives and climate solutions, such as passive cooling, research and implementation emerging carbon equivalency technologies. They can also assist major polluters in offsetting their greenhouse gas emissions.
Supporting Sustainable Development:
VCCs can contribute to sustainable development goals by supporting biodiversity conservation, social and economic development, and clean energy. For example, certain carbon projects aim to protect and restore ecosystems, providing livelihood opportunities for local communities.
Tax Deductions:
VCCs may be eligible for tax deductions if they can be considered a current ordinary and necessary expense.
Our top priority is the development and implementation of a comprehensive global action plan aimed at executing an international program for the installation of cool roof reflective nano-paint.
“One urbanization at a time”
MACOMA invites interested parties to participate in and actively support our large-scale community projects. These large-scale projects can support cooling the earth by increasing mean surface global albedo.
We have cooperative agreements with municipalities to complete the projects, but they cannot be deployed without investment from the Voluntary Carbon Market.
By investing in the purchase of carbon credits associated with the high-albedo roof initiatives, individuals and organizations can contribute to environmental sustainability and promote the adoption of innovative technologies in urban communities.
Participating in these projects aligns with the global imperative to combat climate change. Through collaboration and investment, stakeholders can be pivotal in driving positive environmental impact, promoting sustainable urban development, and fostering resilient communities.
Without monetary investment, these large-scale projects cannot be started or completed.
An innovative method to calculate CO2 offset from high-solar reflective surfaces.
In hot climate regions like much of Latin America, a sizable portion of the energy supply—approximately half—is dedicated to cooling indoor spaces in homes and businesses. This heavy reliance on cooling systems places considerable strain on local economies. It perpetuates a cycle where the carbon dioxide emissions required to power these cooling mechanisms contribute to escalating temperatures. Consequently, the demand for cooling energy intensifies, perpetuating a loop of increased carbon emissions and heightened warming. This interconnected cycle underscores the urgent need for sustainable solutions to break the cycle of escalating energy consumption and environmental degradation in these regions.
Studies from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, in California, underscore the potential of solar-reflective roofing in mitigating these challenges. They reported that the widespread adoption of reflective roofing could yield a global cooling effect equivalent to removing 44 gigatons of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. To put this into perspective, it equates to eliminating the emissions of 600 million cars over a span of 20 years. Furthermore, high solar-reflective roofs, also referred to as high-albedo, passively cool the interior of the structures, saving energy.
At the Urban Heat Island Conference hosted at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, from December 4-7, 2023, distinguished climate scientist and Nobel laureate Prof. Hashem Akbari, PhD, unveiled his latest research on calculating carbon offsets. The study is titled “A Simplified Method to Calculate Atmospheric CO2 Equivalency for Changing Surface Albedo.” This research, authored by Hashem Akbari and the Heat Island Group at Concordia University in Montreal, Canada, introduces a straightforward methodology for determining the atmospheric CO2 equivalency associated with altering surface albedo.
According to H. Akbari’s research presented in Melbourne in 2023, the implementation of high-albedo urban surfaces not only facilitates passive cooling but also generates an additional environmental benefit. By reflecting a greater portion of solar shortwave radiation back into space, these surfaces create a negative radiative force (RF). This counteracts the RF induced by the accumulation of greenhouse gases, primarily CO2, in the atmosphere.
In their study, H. Akbari and colleagues calculated using data from approximately 4400 weather stations worldwide. Their findings revealed that for every 0.01 increase in surface albedo, the median CO2 offset globally amounted to about 2 kg per square meter. Notably, regions with higher atmospheric transmittance, particularly those characterized by hot weather climates, demonstrated the highest levels of CO2 offset. This emphasizes the significant potential for mitigating carbon emissions through the widespread adoption of high-albedo urban surfaces, particularly in areas with elevated temperatures.
contact us

Headquarters
Applied Research Facility
1664 N Virginia St # 112
Reno NV 89557, USA
+1 775-410-2408
+1 702-951-1401
contactus@macoma.us
Argentina Branch
Parque Industrial de la Innovación Posadas
229 Nemesio Parma 3300
Posadas, Misiones, Argentina
+54 3764 63-5556
+54 3764-489717
